Diagnosis and Treatment for Retinal Detachment
People who have severe eye injury, previous detachment in another eye, family history of detachment, who are taking glaucoma medications, weak areas in retina, glaucoma and nearsightedness have increased risk of retinal detachment.
If you have any of these symptoms, seek medical assistance immediately. Always undergo dilated eye exams at regular time intervals, if you are suffering from conditions like nearsightedness or other retinal problems. To safeguard your eyes from serious injury, always wear protective eye wear while doing any hazardous activities or playing sports.
Retinal Detachment Diagnosis:
The pupil is dilated to examine the eyes for any tear or detachment in the eyes by ophthalmologist. To get additional details about the retina, ultrasound scan is also taken. The retinal tear or detachment is only found after a thorough examination and so it is important to have regular eye examinations.
Retinal Detachment Treatment:
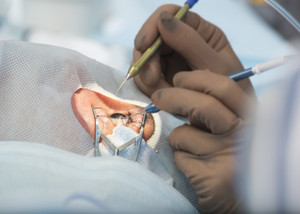
Surgical procedure is the only option to repair a tear or detachment. The ophthalmologist would recommend any procedure based on the condition, keeping in mind the risk associated and benefits.
Torn retina surgery:
In this procedure the retina is sealed with the help of cryotherapy or laser surgery to the eyes back wall. In both the procedures, a scar is formed. This procedure is done to stop fluid from flowing along the tear, as the fluid is responsible for preventing the retina from getting detached.
Laser surgery or photocoagulation is another procedure in which a laser is used to make a small burn on the retinal tear and to seal the underlying tissue. This prevents the retina from getting detached.
Freezing treatment or cryopexy is another procedure in which a special freezing probe is used to freeze the retinal around the retinal tear area. The resultant scar attaches the retina to the eye wall.

 Jul 9th 2020
Jul 9th 2020